Customer Master Data
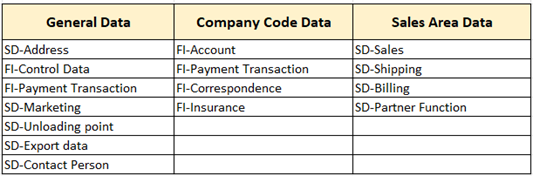
The Customer Master is a centralized data repository in SAP that contains all the information about customers necessary for processing sales and distribution transactions. It is the backbone of the Order-to-Cash (O2C) process and integrates with both SD and FI modules it’s containing customer information such as name, address, contact details, payment details, and sales details. The customer master is divided into three views: general data, company code data, and sales area data
“Master the structure and setup of Customer Master data to ensure seamless sales operations and accurate financial integration. A well-maintained Customer Master is your key to a smooth and efficient Order-to-Cash process.”
Components of Customer Master
The Customer Master is structured into three main areas:
General Data: Common data shared across company codes and sales areas (e.g., name, address, contact info).
Company Code Data: Accounting-related information like reconciliation account, payment terms, and dunning.
Sales Area Data: Sales-specific details such as pricing, shipping conditions, and delivery priority.
Key Fields in Customer Master
Several fields are crucial in ensuring the right setup:
Account Group: Controls field selection, number assignment, and partner determination.
Number Range: Determines how customer numbers are generated.
Partner Functions: Define roles like Sold-to Party, Ship-to Party, Bill-to Party, and Payer.
Tables in Customer Master
Table will help to store the data
T-Code: BP
KNA1 – General data
KNB1 – Company code data
KNVV – Sales area data
KNVP – Partner data
ADRC – Address data
VBKD – Business data
Configuration Behind the Customer Master
Step 1: Define Number Ranges for Customer Group
T-Code: XDN1.
Create number ranges (e.g., 01 to 1000000) and Internal or external number assignments.
Step 2: Define Customer Group and Assign Number Range to Customer Group
T-Code: OVT0
Create or modify an account group (e.g., Z001) and assign your number range.
Step 3: Define Partner Determination Procedure
T-Code: VOPA
Define Partner Functions (e.g., Sold-to, Ship-to, Bill-to, Payer).
Create Partner Determination Procedure (e.g., ZPP).
Assign partner functions to the procedure and assign the procedure to the account group.
Step 4: Create Number Range for Grouping BP
T-Code: BUCF
Create number ranges for BP (internal/external).
Example: 1000000000 to 1999999999
Step 5: Define Grouping and Assign Number Range
T-Code: BUCF
Groupings correspond to account groups and control number range assignment.
Example Grouping: ZDOM -> Domestic Customers
Assign number range to the grouping
Step 6: Define Number Assignment for Direction BP to Customer
“Cross-Application Components -> Master Data Synchronization -> Customer/Vendor Integration -> Business Partner Settings -> Synchronization Control -> Define BP Role for Direction Customer to BP”
Map BP Grouping -> Customer Account Group
Example: BP Grouping: ZDOM and Customer Account Group: Z001
Benefits of Customer Master
Faster Order Processing
Accurate customer data ensures that sales orders can be created and processed without delays or manual corrections.
Reduced Billing Errors
Correct billing details like payer, tax classification, and payment terms minimize invoice disputes and rework.Improved Delivery Accuracy
Valid shipping addresses and contact details help avoid delivery failures and customer dissatisfaction.
Enhanced Customer Service
With updated contact and transaction history, support teams can respond quickly and accurately to customer inquiries.
Common Issues with Customer Master
Duplicate Customer Records
Happens when users create new entries without checking for existing ones.Incomplete Master Data
Missing key fields like sales area data, payment terms, or tax info can block sales orders or invoices.Incorrect Partner Functions
Wrongly assigned Bill-to, Ship-to, or Payer functions lead to billing and shipping errors.Inconsistent Data Across Sales Areas
Same customer has conflicting data in different sales areas, creating confusion and errors.
Conclusion
The Customer Master in SAP SD is much more than a data table—it's a foundation for customer relationships, operational accuracy, and financial efficiency. Proper configuration and maintenance not only prevent errors but also unlock faster, smarter business processes.
“Master the customer master process to enable smooth sales operations. Use it as a strategic tool to enhance customer service and business control.”