Debit & Credit Note
Introduction
In business transactions, invoices often require adjustments due to errors, changes in agreements, or returns. To avoid cancelling and recreating entire invoices, organizations use Debit Memos and Credit Memos. These documents simplify corrections in financial records while maintaining transparency and compliance. In SAP, debit and credit memos are part of both Sales and Distribution (SD) and Materials Management (MM) modules.
Concept of Debit and Credit Note
Debit Memo: A debit memo is issued to a customer when further payment is required. This could be due to:
The original invoice amount was undercharged.
Further goods or services were delivered beyond the original billing.
Shipping or additional fees were omitted from the original invoice.
Customer pays more: It increases the customer’s payable balance or reduces the vendor's receivable balance.
Credit Memo: A credit memo is issued when a customer has an overpayment or the invoice amount needs to be corrected. This might happen when:
The original invoice was overcharged.
The customer returned the goods.
Discounts or rebates need to be applied.
Customer pays less: It decreases the customer’s payable balance or increases the vendor’s receivable balance.
Both serve as adjustment mechanisms to ensure financial accuracy without reissuing the base invoice.
Why They Are Important
Accuracy in billing: Correct mistakes in original invoices without full cancellation.
Transparency: Provides a clear audit trail for adjustments.
Customer/vendor trust: Shows professionalism in handling disputes and errors.
Compliance: Aligns with accounting standards and internal control procedures.
Efficiency: Saves time compared to regenerating entire invoice cycles.
Real Time Scenarios
Debit Memo / Debit Note: A sale of ₹5,000 was made, but ₹500 for delivery charges was not included. To make up for this, a debit memo is sent to the customer, asking for the extra ₹500.
Credit Memo / Credit Note: A customer was billed ₹1,000 for 10 units, but they sent back 2 defective units. The seller issues a credit memo for ₹200 to rectify the overbilling.
Benefits of Debit and Credit Memos in SAP
Accurate Financial Records: Ensure invoices reflect the correct amount without cancelling and recreating them.
Time & Cost Efficiency: Save effort by quickly correcting billing errors instead of regenerating full invoices.
Compliance & Transparency: Provide a clear audit trail that supports accounting standards and internal controls.
Better Customer & Vendor Relationships: Build trust by handling overcharges, undercharges, and returns promptly.
Improved Cash Flow & Reconciliation: Speed up collections for additional charges and reduce disputes during payment cycles.
Common Problems
Overuse of memos: Too many adjustments may signal weak billing practices.
Disputes: Customers/vendors may contest debit memos if not well justified.
System mismatches: Incorrect configuration can result in posting errors.
Delayed processing: Can affect payment cycles and financial reporting.
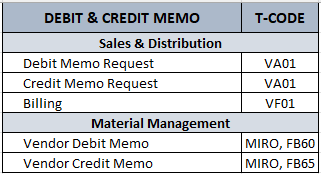
Transaction Codes
Sales & Distribution (SD)
Debit Memo Request: VA01
Credit Memo Request: VA01
Billing: VF01
Materials Management (MM)
Vendor Debit Memo: MIRO, FB60
Vendor Credit Memo: MIRO, FB65
Configuration
Step 1: Define Document Types
SPRO → Sales and Distribution → Billing → Define Billing Types.
Create Debit Memo Request (DR) and Credit Memo Request (CR).
Step 2: Assign Number Ranges
Assign unique ranges for debit/credit memo documents.
Step 3: Copy Control Settings
Define copy control from sales order to billing and billing to accounting.
Step 4: Posting to Accounts
Ensure correct GL accounts are assigned for revenue adjustments.
Step 5: Process Flow (SD)
Create Debit/Credit Memo Request (VA01)
Create Billing Document (VF01)
Post to FI automatically.
Example Scenarios for Debit & Credit Memo
1. Sales & Distribution (SD)
Debit Memo Scenario (SD)
Business Case: A company sells 100 units of a product at ₹500 each (₹50,000 total). Later, it realizes that packaging charges of ₹2,000 were missed in the invoice.
SAP Flow:
Create a Debit Memo Request in VA01 (document type DR).
Convert the request into a Billing Document using VF01.
The customer now receives an additional invoice of ₹2,000.
Result: The Customer’s payable increases, correcting the underbilling.
Credit Memo Scenario (SD)
Business Case: A customer orders 50 units at ₹200 each (₹10,000). Out of these, 5 units are defective and returned.
SAP Flow:
Create a Credit Memo Request in VA01 (document type CR).
Convert the request into a Billing Document using VF01.
The customer receives a refund/adjustment of ₹1,000.
Result: The Customer’s payable decreases, ensuring fairness and accuracy.
2. Materials Management (MM)
Debit Memo Scenario (MM)
Business Case: A vendor supplies 500 raw material units at ₹50 each (₹25,000). Later, freight charges of ₹2,500 were missed.
SAP Flow:
Post the vendor invoice using MIRO.
Create a Debit Memo against the vendor for the extra freight cost.
Vendor’s payable amount increases by ₹2,500.
Result: The Company pays the vendor the correct total amount.
Credit Memo Scenario (MM)
Business Case: A vendor delivers 1,000 items at ₹100 each (₹100,000). After GR (Goods Receipt), 100 items are found defective and returned.
SAP Flow:
Post the original invoice using MIRO.
Create a Credit Memo in MIRO or FB65 for 100 items (₹10,000).
Vendor’s receivable decreases by ₹10,000.
Result: The company pays less to the vendor since defective goods were returned.
Conclusion
Debit and Credit Memos in SAP provide businesses with flexible tools to maintain financial accuracy without reissuing full invoices. They allow quick corrections for underbilling, overbilling, returns, or additional charges while ensuring compliance and transparency. When configured and used correctly, they improve efficiency, strengthen customer/vendor relationships, and support accurate financial reporting.