Sales Document Types
In the world of SAP Sales and Distribution (SD), Sales Document Types form the foundation of every sales transaction. Whether it’s creating a sales order, managing deliveries, or generating billing documents, the sales document type determines the rules and controls behind each process. By configuring document types properly, organizations can ensure smoother sales operations, compliance with business rules, and better data accuracy.
This blog will walk you through the purpose, importance, common issues, key T-codes, and step-by-step configuration of sales document types in SAP SD. By the end, you’ll have both a conceptual understanding and a hands-on guide to managing sales document types effectively.
Purpose of Sales Document Types
The purpose of sales document types is to provide structure and control to different kinds of sales transactions. For example:
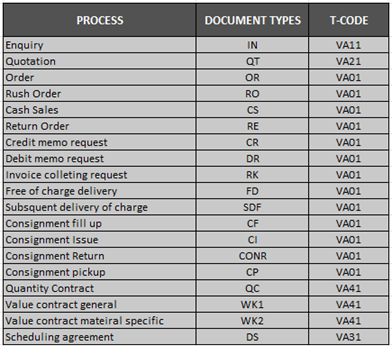
OR (Standard Order): Used for regular customer sales.
RE (Returns): Used for customer returns and credit processing.
CR (Credit Memo Request): For handling billing corrections or post-sales adjustments.
Each type defines specific business rules like pricing procedure, delivery relevance, billing type, and partner functions. This ensures consistency and accuracy across business processes.
Importance
Sales document types play a critical role in streamlining operations:
Control over processes: Define which steps (delivery, billing, credit check) are required.
Flexibility: Customize document types to meet unique business requirements (e.g., export orders vs. domestic orders).
Error reduction: Prevents users from making incorrect entries by enforcing defaults and restrictions.
Integration: Ensures smooth flow of data between SD, MM (Materials Management), and FI (Financial Accounting).
Reporting and analysis: Segregating sales transactions by document type allows meaningful reporting.
Common Issues
While configuring sales document types, consultants and users often face these challenges:
Incorrect number range assignment (VN01): Leading to missing or duplicate document numbers.
Improper sales area assignment (OVAZ): Resulting in errors when creating orders.
Pricing or delivery relevance not defined properly: Causing incorrect billing or blocked orders.
Too many custom Z-document types: Overcomplicating processes and creating maintenance headaches.
Tip: Always review whether a standard document type can be reused before creating a custom one.
Sales Document Types:
Sales Document Types
Key T-Codes for Sales Document Types
Here are the most important transaction codes you’ll use while configuring sales document types:
VOV8 – Define Sales Document Types
OVAZ – Assign Sales Document Types to Sales Area
VN01 – Define Number Ranges for Sales Documents
SPRO (IMG path): Sales and Distribution > Sales > Sales Documents > Sales Document Header > Define Sales Document Types
These T-codes are essential for both initial setup and troubleshooting.
Scenario
Sales Document Types T-Code
Step-by-Step Configuration
Let’s go step by step into configuring a new sales document type:
Step 1: Define Sales Document Type (VOV8)
Go to SPRO > IMG > Sales and Distribution > Sales > Sales Documents > Sales Document Header > Define Sales Document Types.
Create a new document type (e.g., ZOR for customized order).
Set the following parameters:
Item number increment (e.g., 10, 20, 30…)
Order type text (for identification)
Delivery and billing relevance
Reference mandatory (if applicable)
Step 2: Assign Sales Area (OVAZ)
Combine the Sales Organization, Distribution Channel, and Division.
Assign the new document type (e.g., ZOR) to the relevant sales area.
Step 3: Define Number Ranges (VN01)
Create a new number range for sales orders.
Assign the range to your sales document type using VOV8.
Step 4: Test the Configuration
Create a new sales order using VA01.
Select your new document type (ZOR).
Validate the order flow (pricing, delivery, billing).
Real-Time Example
Suppose your company handles online retail sales and bulk export orders. For online sales, you may want to use a standard order type (OR) with immediate billing. For exports, you may create a custom order type (ZEX) with special pricing and mandatory export documentation. By configuring sales document types properly, you can streamline both processes without confusion.
Conclusion
Sales document types are building blocks of SAP SD that define how different sales scenarios are handled. From ensuring proper control to enabling flexibility, they form a crucial part of the sales cycle. By mastering T-codes like VOV8, OVAZ, and VN01, and by following a step-by-step configuration process, you can customize SAP SD to meet your organization’s needs.